Data speak: Where does China’s economic stability come from?
Recently, China’s economic indicators from January to July were released one after another, which aroused a lot of concern.
As the largest trading partner of more than 120 countries and regions in the world, the next trend of China’s economy affects the pulse of the global economy.

In the past ten years, the air routes of 11 international hub ports along the coast of China have increased by 60%. The maritime service network connects the major ports of more than 100 countries and regions, making it the country with the highest maritime connectivity in the world.
At present, the century-old changes and the century-old epidemic are intertwined, and countries around the world are deeply impacted. How should we understand the challenges that China’s economy is experiencing and the expectations of future growth?
And how to find the right coordinates to evaluate China’s economy?
Master Tan worked out an account with the authority.
01
Which epidemic prevention and control mode has the lowest cost?
A research team of the National Bureau of Statistics has made a model calculation on the relationship between epidemic prevention and control policies, macroeconomic policies and economic loss rate in various countries since the outbreak of the COVID-19 epidemic. The results show that:
From 2020 to the first half of 2022, the total economic loss rate of China was only 2.3% under strict prevention and control.
However, the economic loss rate under tight prevention and control (such as Japan and South Korea), passive prevention and control (such as Germany and France) and passive prevention and control (such as the United States and Britain) reached 3.9%, 5.5% and 5.9% respectively.

At the same time, after excluding the impact of macroeconomic policies, China’s economic loss rate dropped to.floor level.
The international media pointed out in an article entitled "China’s policy of" dynamic clearing "of COVID-19 infection contains lessons for other countries" that China’s anti-epidemic policy of "dynamic clearing" has achieved the goal that every country sought two years ago: low mortality and as little economic chaos as possible.
China’s epidemic prevention model has been achieved.Give consideration to anti-epidemic and production developmentThe effect.
A typical example is that in the first half of this year, China’s export data became the bright spot of growth, while the economic growth expectations of major countries in the world were declining.
02
Why has China become a global lifeline?
This is one of the perspectives of epidemic prevention cost accounting. China insists on "dynamic zero clearing", which reduces the manpower, material resources and economic and social costs as much as possible, in exchange for overall economic and social stability.
Behind China’s low economic loss rate is the stability and toughness of China’s supply chain and industrial chain under the policy of "dynamic clearing".
In the past two years, repeated outbreaks have made this more prominent.
Recently, Tan Zhu chatted with Yan Ci, the chief representative of China, the global container shipping logistics giant Maersk Group.
The year when Maersk invested in the first fully automated storage project in China was 2020, when the epidemic had just begun.
Maersk has a reason to dare to cast this project against the wind.
At the China International Fair for Trade in Services in 2020, Yanci praised the company for maintaining normal operation and uninterrupted supply chain with the help of China government.
During the epidemic, China fully guaranteed the production of enterprises with a stable soft and hard environment. The goods manufactured in China are continuously transported to the world through logistics companies like Maersk.
According to the statistics of the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development,During the epidemic, China’s share of global merchandise exports increased from 13% in 2019 to 15% by the end of 2021..
Among them, China’s share in global electronic products exports increased from 38% in 2019 to 42% in 2021, and its share in textile exports increased from 32% to 34%.
China’s increased export share has become the "lifeline" for countries such as the United States and Britain to maintain their operations.
In 2020, when the epidemic just broke out, 83% of the imported masks in the United States were made in China, two-thirds of the protective clothing came from China, and 90% of the imported box refrigerators specially used for storing vaccines came from China, showing an explosive growth.
The epidemic prevention and control in China has stabilized the industrial chain and supply chain, making China a ballast stone to meet the needs of global epidemic prevention, production and life.
Stability in the face of wind and rain comes from the accumulation of a sword in ten years.The "Decoding Decade" broadcast by the main station is the best example.

Despite the epidemic, the number of China-Europe trains that are still running smoothly in the Eurasian continent has exploded in this decade, reaching nearly 900 times that of the opening year. Now, there are an average of 42 trains running between China and more than 190 European cities every day.
In the complicated global epidemic situation, stable policies and environment are more attractive, and the keen international capital flow is very convincing.
A few days ago, the Ministry of Commerce announced that from January to July this year, the actual amount of foreign capital used nationwide was 798.33 billion yuan, an increase of 17.3% on a comparable basis.
Investment is confidence.
03
Who has more confidence in China?
You can look at the four sources of investment in China highlighted by the Ministry of Commerce:

The United States, which has failed to prevent and control the epidemic, has increased its investment in China by 36.3%, and the rest of the countries are also allies that the United States is trying to win over.
You know, for a long time in the past, a focus of American diplomacy was to build small courtyards and high walls on the industrial chain with these countries as the axis.
But what is it?as the trend of the times indicatesMultinational enterprises have given their choices by voting with their feet.
According to the 2022 White Paper on American Enterprises in China released by the American Chamber of Commerce in China this year, more than two-thirds of the member companies continue to list China as the primary market.
Starbucks, a Seattle-based coffee chain, is committed to opening 6,000 stores in China before the end of the year.
Germany, in the first half of this year, set a record high for its investment in China in the first half of this year since 2000. Among the industries in which Germany increased its investment in China, there was its manufacturing "crown jewel" — — Automobile industry.
This year, German Volkswagen, which has been producing and operating in China for nearly 40 years, set the first subsidiary of its software company CARIAD in China — — This is also CARIAD’s first overseas subsidiary.
Nearly 40 years ago, the presence of Volkswagen once planted the seeds of growth for China automobile industry.
Today, in the eyes of the public, the establishment of a new factory in China, which ranks first in the world in the new energy automobile industry, represents the hope of the public.
Bringing the "leader" of China’s top industries to China means more precious confidence besides economic considerations.
From a global perspective, the United States, Japan, South Korea and Germany are the economic leaders in America, Asia-Pacific and Europe respectively, and they are also the weathervanes in their regions. Their choices are very convincing.
In fact, the Americans themselves have long forgotten: China is one of the countries with the highest total rate of return on foreign direct investment in the United States.
According to the U.S. Department of Economic Analysis, from 2000 to 2020, the average rate of return on American direct investment in China is14.7%, much higher than the US overseas direct investment.9.7%Yield.
On the contrary, if American companies reduce their investment in China by half, it will cause very direct damage to the American economy, and the one-time loss of gross domestic product (GDP) will be as high as 500 billion US dollars.
Even during the COVID-19 epidemic, the overall rate of return of foreign investment in China is still rising. In 2021, foreign investors can still get a rate of return of over 6% when they invest in China.

From a longer time dimension, the rate of return on investment in China in 2020 and 2021 remains at a stable level compared with before.
Under the epidemic, it remains stable, which is very telling.
Pan Yuanyuan, an international investment expert at China Academy of Social Sciences, told Tan Zhu:
The first characteristic of foreign direct investment is the long time period; Second, foreign-funded enterprises will also participate in management, bringing their own technology, experience and channels to China, and combining them with China’s resources for transformation. Therefore, unlike short-term speculative investment in the securities market, direct investment pays more attention to the fundamentals of the economy and is also more alert to risks and uncertainties.
In other words, the most important thing for foreign direct investment is the stability of a country’s economic expectations.
04
Where does the stability of China’s economic expectations come from?
Recently, the International Monetary Fund also increased the RMB weight in the Special Drawing Rights (SDR) from 10.92% in 2016 to 12.28%.
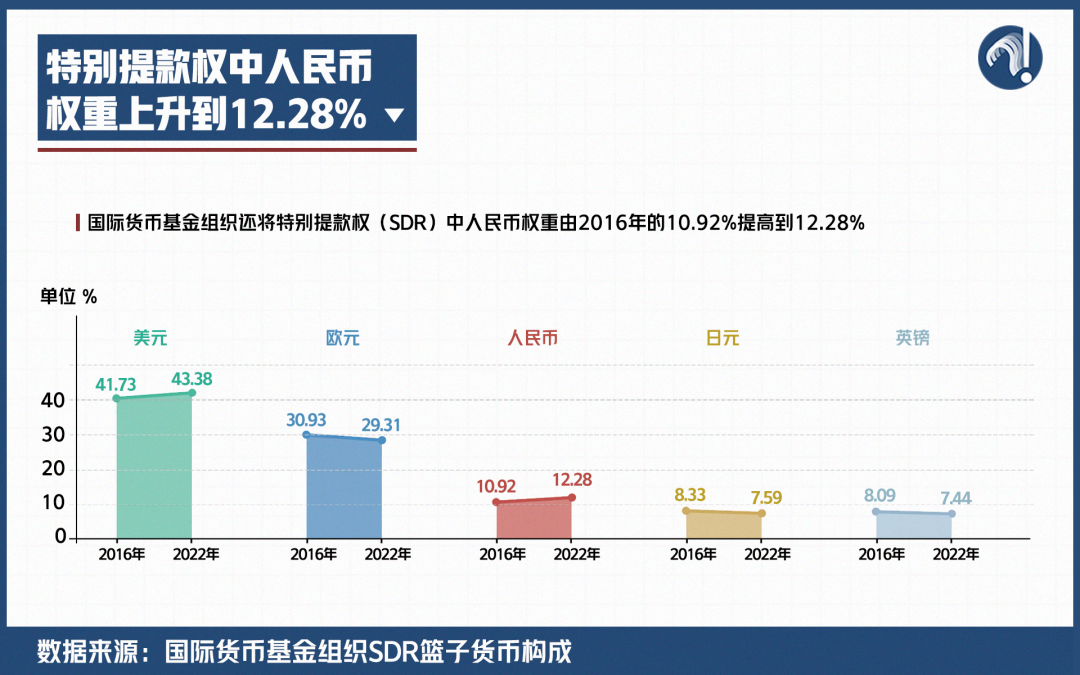
This figure is the confidence of the international community in the stability of China’s economy and financial market, and also the recognition of effective epidemic prevention and control in China.
In 2020, under the epidemic crisis, countries’ economic policies to deal with the impact are completely different.
Countries represented by the United States, passive prevention and control, but in order to get quick results in the short term, have adopted unlimited quantitative easing policies.
From the second quarter of 2020 to the first quarter of 2021, the year-on-year growth rate of M2 in the United States remained above 20%, and the average growth rate of M2 after the epidemic was about 10 percentage points faster than that before the epidemic.
Moreover, the United States has repeatedly introduced large-scale economic rescue bills. In 2021, the fiscal deficit ratio reached 12.4%, even higher than the historical high of 9.8% during the financial crisis in 2009.

The "strong medicine" seems to be effective quickly, but it has led to bad consequences.
During the epidemic, the United States not only ranked among the countries involved in the survey with an economic loss rate of 6.5% (excluding the impact of macroeconomic policies). The more direct performance is that the inflation level in the United States has reached a 41-year high.

Inflation in the United States not only makes American enterprises and consumers bear high production and living costs, but also transfers the crisis to the whole world.
According to the assessment of the Bank for International Settlements, the annual inflation rate of nearly 60% developed economies exceeds 5%, the highest level since the late 1980s. The inflation rate of more than 50% developing countries has also exceeded 7%.
The rapid interest rate hike by the Federal Reserve in response to inflation has expanded the debt scale of emerging market countries. According to the International Monetary Fund, there are currently 38 developing countries facing debt risks.
Under the impact of global inflation and the Federal Reserve’s interest rate hike, Sri Lanka was forced to declare bankruptcy due to "insolvency" and became the first new market country to default on its sovereign debt in 2022.
Compared with the strong stimulus measures of the United States, during the epidemic, China’s macroeconomic policies were always guided at a steady pace. In the first half of this year, the national consumer price index (CPI) rose by 1.7% year-on-year, far below the level of European and American countries.
Because of this, the US dollar index has risen by more than 11% this year, and the depreciation of the euro, pound and yen against the US dollar is between 10% and 17%. Compared with these major global currencies, the performance of RMB is relatively stable — — It depreciated by about 5.8% against the US dollar.
As Lu Jinyong, director of the university of international business and economics Foreign Direct Investment Research Center, said, China still gives people an expectation and hope — — A growth expectation, profit expectation and better and better hope.
One of the articles in the international media commenting on China’s economy was titled "China’s economy has hidden power".
What are the hidden forces of China’s economy?
It is to plan development and safety as a whole, and it is a prominent problem to deal with economic development with systematic concept.
It is the wind and waves that are high, but it is as tough as a rock, and it is slow and steady, and it has its own sky.